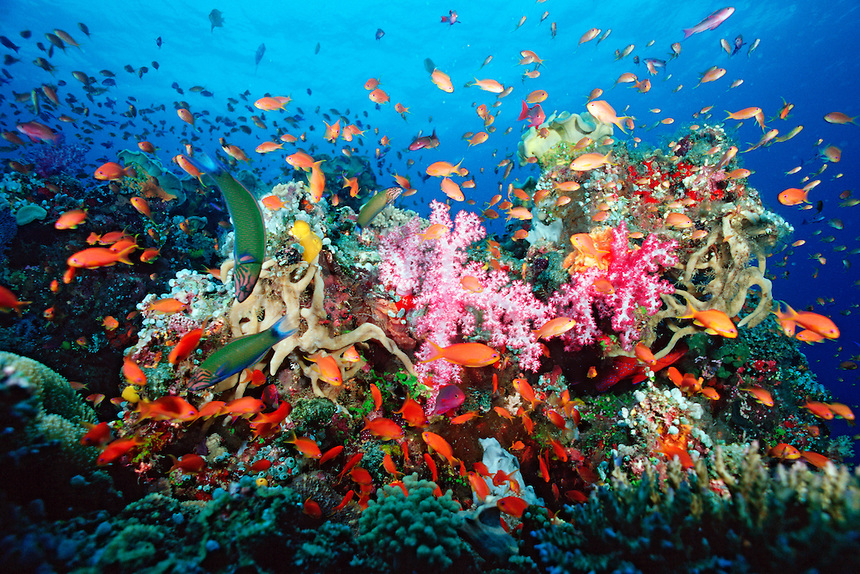
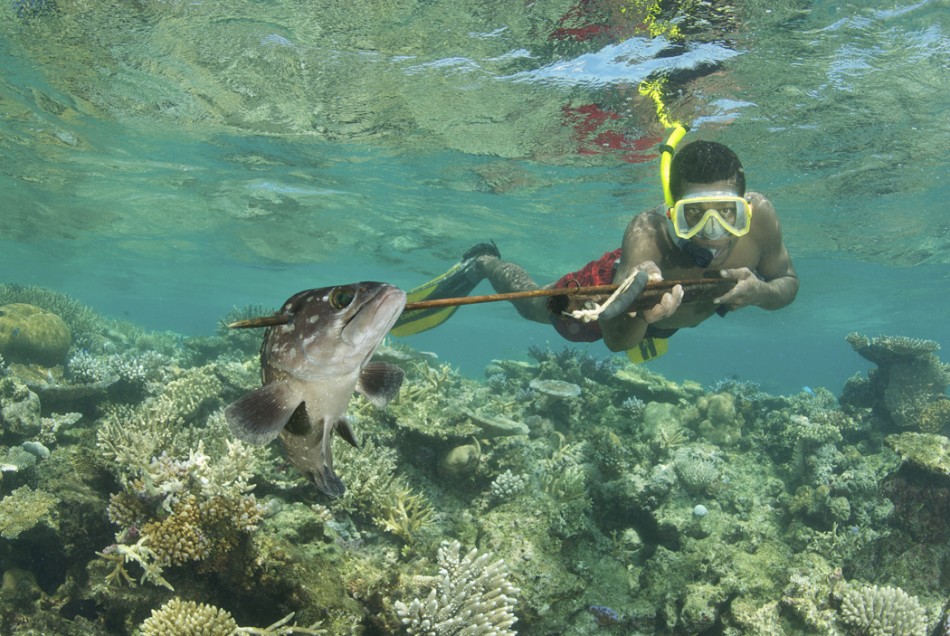
Many of the past studies discussed in previous posts mentions that such impaired behaviour will increased predator mortality. As such future populations are likely to decrease. The podcast with Dr Pippa Moore discusses the implications that such decreases in populations will have on the reef ecosystem.
However reef ecosystems, being such a rich source in terms of biodiversity, have enticed us to utilise this environment as a food supply. With the majority of reef habitats located in shallow areas they are often located near land on continental shelves (as shown in the map below).
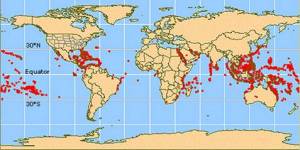
This enables them to be easily accessible to humans to utilise such a plentiful supply of resources. In addition these tropical reefs occur around the equator typically in lower developed countries making them a vital food supply for subsistence farming.
It is estimated that 30 millions fishers in the developing world, rely on reefs for food, survival, and a livelihood. UNEP-WCMC (2006).
Such a significant statistic means that future losses of tropical fish populations will affect humans reliant upon the reef environment as a vital food source.
References and Extra reading
Cover image taken from:http://voices.nationalgeographic.com/2011/05/31/expedition-begins-to-sacred-reef-of-fiji/subsistence-fishing-a-local-fijian-spearfisherman-catches-a-whitespotted-grouper-epinephelus-caeruleopunctatus/
National Ocean Service. (2008). The majority of reef-building corals are found in tropical and subtropical waters. [online image]. Retrieved October 24, 2014 from http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/education/kits/corals/media/supp_coral05a.htm
UNEP-WCMC (2006) In the front line: shoreline protection and other ecosystem services from mangroves and coral reefs. UNEP-WCMC, Cambridge, UK 33 pp.

